Testicular descent: age, anomaly, operation
The descent of the testicles is from the abdomen to the scholarships during fetal life and until the age of 6 months on average.What to do in the event of an anomaly or testicle not descended?What are the treatments ?When to consider an operation?Explanations from Dr. Paula Borrego, pediatrician surgeon, in Paris.
Definition: What is testicular descent?
The testicles are formed during fetal life inside the abdomen."They carry out a migration under hormonal influence which bring them to the bottom of their respective scholarships via the groin, explains Dr. Borrego. These protect them and maintain them at a temperature between 34 and 36 °".This migration phenomenon, also called "testicular descent", is essential for their proper functioning as well as reproduction.Only, it happens that it does not happen properly (for a testicle, even both).
At what age descend the testicles?
The testicular migration begins from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy.If it most often takes place during pregnancy, it can happen that it occurs shortly after."The not descended testicle is a frequent situation: it affects approximately 3 to 5 % of newborns and 30 % of the prematureates, specifies Dr. Berrego. In half of the cases, migration will finalize spontaneously during the 6First months of life, sometimes a little later, especially in the event of prematurity. If this is not the case, surgical management is organized before the age of 1 year ".
Malted testicle: what anomalies?
The causes are multiple and not yet all clearly identified.Are mentioned:
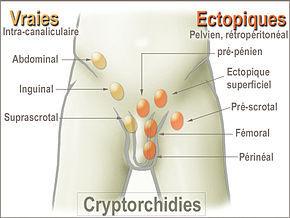
"Note that in the event of a non-palpable testicle, it can be in the abdomen or non-existent, because either its training has not led or it occurred a prenatal testicular torsion accident or in the month whichfollowed the delivery, "says Dr. Borrego.
How to make the diagnosis?
At birth, during the systematic clinical examination before the release of maternity, the position of the testicles is sought.If the testicle is not in place, new assessments will be done regularly at the time of clinical examinations by the pediatrician or the attending physician during the first months of life."In the event of the persistence of cryptorchidia, a first appointment with a pediatric surgeon around the age of 6 months is recommended to organize care, says Dr. Borrego. No additional examination is necessary (ultrasound...) ".
What are the treatments ?
The treatment is always surgical in the operating room, under general anesthesia and outpatient, with some exceptions."The purpose of the operation is to improve the production process of sperm and prevent the risk of unpaid testicle cancer," said the surgeon.
How is the operation going?
Depending on the case: → For a palpable testicle: a short incision is practiced in the groin in order to release the adhesions preventing the descent from the testicle.An associated hernia is systematically sought and treated at the same time.A second incision is practiced at the stock market to position and fix the testicle. → For a non-palpable testicle: surgical intervention will begin with a laparoscopy (mini-invasive abdomen surgery) explorating, in order to search the testiclein the abdominal cavity."If present, the treatment will depend on its position and the length of the vessels that vascularize it," says Dr. Borrego.
Thanks to Dr. Paula Borrego, surgeon-pédiatre, in Paris.
Descente testiculaire : âge, anomalie, opérationDefinitioningAnomalies Diagnostictraitations Properation Definition: What is testicular descent? Testicles are formed during fetal life within the abdomen."They...
I manage my push subscriptions